
 |
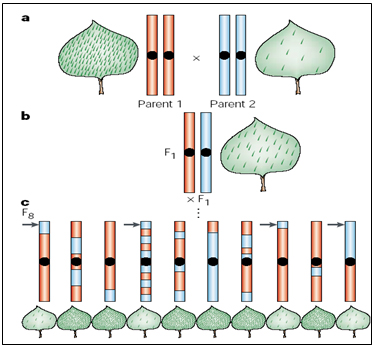
Figure 3. Principles of mapping quantitative trait loci (QTL). (a) Inbred parents that differ in the density of trichomes (parent 1: high trichome density; Parent 2: low trichome density) are crossed to form an F1 population with intermediate trichome density. (b) An F1 individual is selfed to form a population of F2 individuals. (c) Each F2 is selfed for six additional generations, ultimately forming a set of recombinant inbred lines (RILs). Each RIL is homozygous for a section of a parental chromosome. The RILs are scored for genetic markers, as well as for the trichome density phenotype. In (c), the arrow marks a section of chromosome that derives from Parent 2 (the parent with low trichome density). The leaves of all individuals that have inherited that section of chromosome from the parent with low trichome density also have low trichome density, indicating that this chromosomal region probably contains a QTL for this trait (Mauricio, 2001). |
|
|